Low-cost gel film can pluck drinking water from desert air
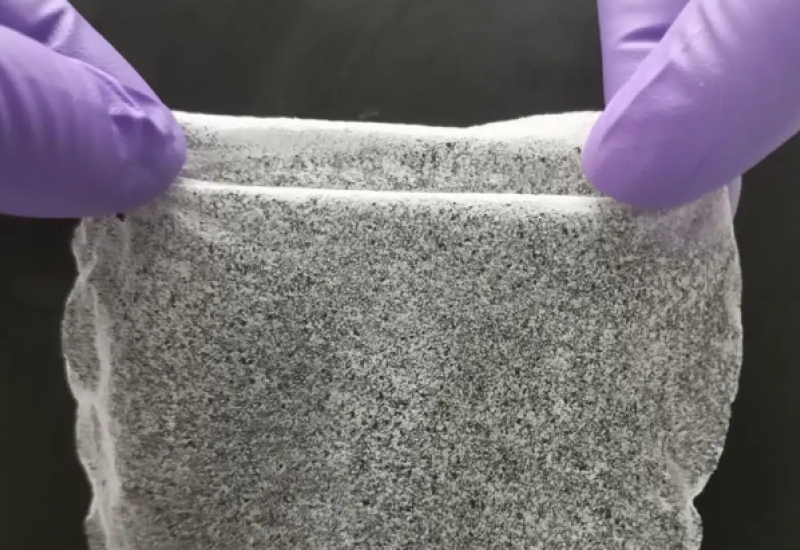

More than a third of the world's population lives in drylands, areas that experience significant water shortages. Scientists and engineers at The University of Texas at Austin have developed a solution that could help people in these areas access clean drinking water.
The team developed a low-cost gel film made of abundant materials that can pull water from the air in even the driest climates. The materials that facilitate this reaction cost a mere $2 per kilogram, and a single kilogram can produce more than 6 liters of water per day in areas with less than 15% relative humidity and 13 liters in areas with up to 30% relative humidity.
The research builds on previous breakthroughs from the team, including the ability to pull water out of the atmosphere and the application of that technology to create self-watering soil. However, these technologies were designed for relatively high-humidity environments.
"This new work is about practical solutions that people can use to get water in the hottest, driest places on Earth," said Guihua Yu, professor of materials science and mechanical engineering in the Cockrell School of Engineering's Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering. "This could allow millions of people without consistent access to drinking water to have simple, water generating devices at home that they can easily operate."
Source: Science Daily
Image: The University of Texas at Austin